
- Linux and mac os program traceroute how to#
- Linux and mac os program traceroute mac os x#
- Linux and mac os program traceroute windows#
To obtain an OpenVPN server with the default behavior, you only need, after you have activated Zeroshell on your network, to enable the OpenVPN service by clicking on the Enabled flag in the -> section of the Zeroshell’s web interface.
Linux and mac os program traceroute how to#
More precisely, we will see how to access to a VPN server builded with ZeroShell and configured with the default parameters. In addition, you could use the openvpn command in a script to automatically start the VPN connection.
Linux and mac os program traceroute windows#
This last possibility is useful, because the openvpn command, which you can execute by using the prompt (Unix Shell or Windows Prompt) accepts the same parameters and has the same behavior regardless from which Operating System you use. At the end of the document we will learn to use the OpenVPN’s command line interface.
Linux and mac os program traceroute mac os x#
We will see how to install and configure the most used OpenVPN’s GUI for Microsoft Windows, Linux, Mac OS X and Windows Mobile for Pocket PC. After entering ‘cmd’ into the opened text box and pushing the ‘Enter’ button, the Windows input prompt opens and the tracert command is now ready to be put in.The purpose of this document is to lead the users to configure theirs OpenVPN clients to access to a VPN server. The easiest way to start cmd.exe is with the keyboard shortcut ‘Window logo key’ + ‘R’. cmd.exe opens a window with the command line and input prompt and displays an extended version of the command line interpreter from MS-DOS. Users of Windows systems first need to enter the tracert command in cmd.exe, which is also known as the Windows command prompt. Execute tracert on Windows operating systems The following is an introduction on how to use tracert and traceroute. Commands need to be manually entered and are executed with the ‘Enter’ button. Entering the command line can only be carried out by using the keyboard. This functions in different ways depending on the operating system in use. In order for the data package to get analyzed using this method, the command line has to be opened. Here is a list of sites that enable trace route tracking: In most cases, the sender address is the web server on which the used website is hosted (not the address of the respective user). Many websites offer the option of tracking the route to the targeted IP address and, to a certain extent, even work with visual traceroute tools that clearly display gathered information. Those wishing to forego the task of dealing with the command line are able to utilize traceroute online.
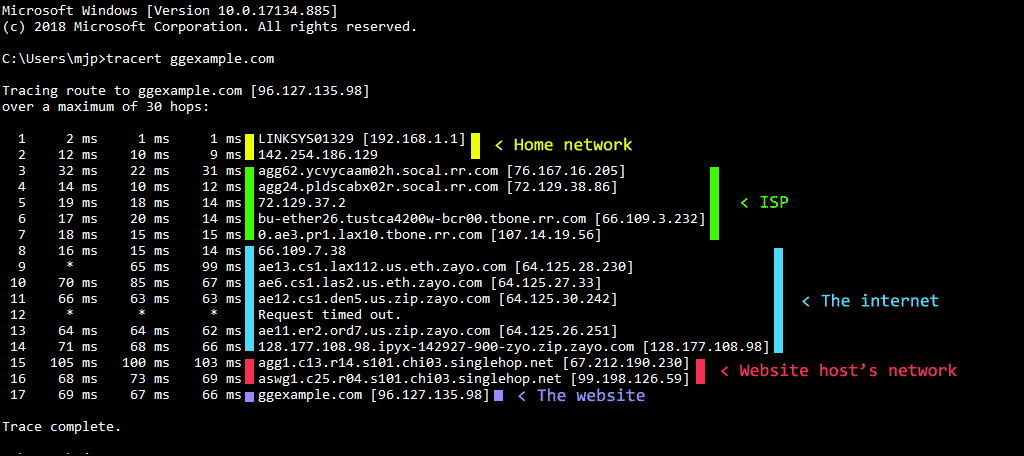
Following its default settings, a total of three packages is sent to each host, which is why traceroute displays three response time statements, all of which are issued to the millisecond. The located host then sends the message ‘Port unreachable’ and terminates registering the IP trace route. This process is repeated until either the target host or the defined maximum number of hops, i.e. Tracert records this information along with the transfer duration and then repeats the process with a TTL raised by the value of 1. Following this, the router devalues the TTL to 0.Īs a result, the data package is no longer forwarded, and the router instead sends the answer ‘Time to live exceeded in transit’ along with its IP address back to the original exit server. The router that is reached first on the way to the target host receives a package with a TTL of 1.
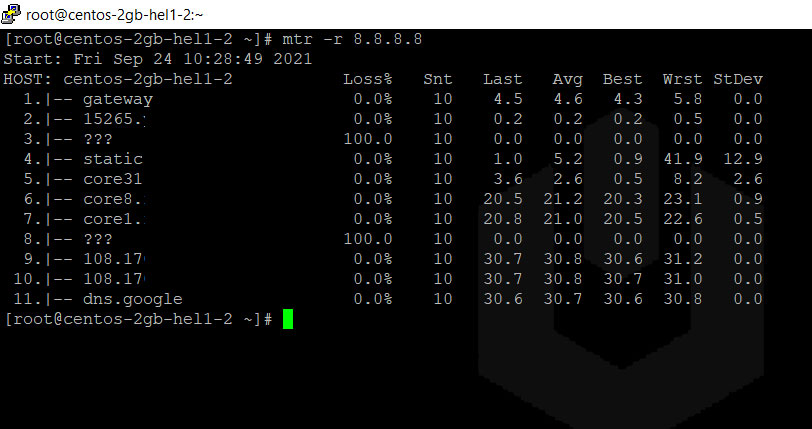
In order to request an answer from the accessed router, tracert sends automatic pings ( ICMP), while traceroute, as programmed by default, sends UDP packages. Every passed router automatically reduces the TTL’s value by 1. Instead, it focuses on the maximum number of stations, or hops, that a given online data package is allowed to cover. Contrary to what its name may imply, TTL does not actually deal with any sort of time units. Traceroute, or tracert, sends small data packages with limited time to live (TTL) to the target host.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
